You are here
Hot Crimping Magnet Wire to Cable Shoes or Terminals
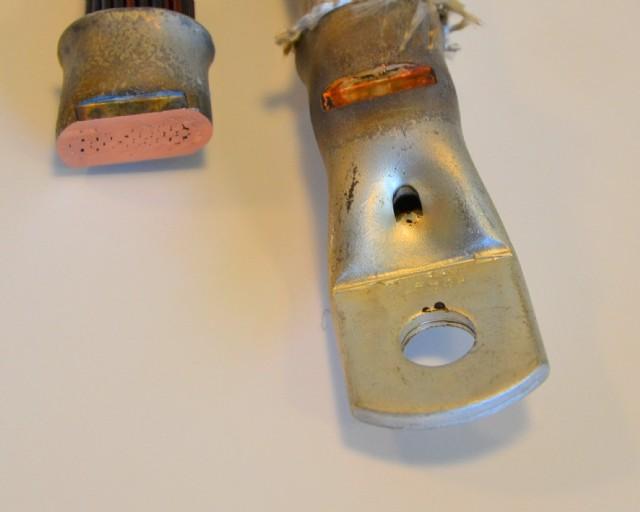
Hot Crimping to Cable Shoes is a metal joining technology that uses electrical current and mechanical pressure to connect electrical conductive wires. Hot crimping is a type of resistance welding. Hot crimping differs from other types of resistance welding because it uses a conductive metal sleeve to pass the current, generate the heat and hold the wires together. This sleeve fuses the wires and makes one compacted metal part. The sleeve can be a cable shoe, a terminal or a simple round sleeve.
The joint is formed using a process called diffusion welding. Diffusion welding means that the copper is joined because the copper wires and the copper connector fuse together at near-to melting temperature. The material stays in the solid phase and never enters the liquid phase.
Hot crimping is similar to resistance welding and relies on the heat generated by the electrical resistance of the material being welded and the force used to hold the materials together during welding. It produces electrical connections with a very high conductivity and nearly zero contact resistance which are free from any significant voltage drop. The hot-crimped joint has very high tensile strength and will not weaken over time due to vibration or temperature as it is one solid piece of metal. The heating causes the metal to anneal and mechanical stress in the joint is relaxed which minimizes stresses on the copper in the wire and terminal after the joining process.
In many cases, these magnet wires are electrical isolated. The insulation may be enamel or a polymer film like polyurethane, polyamide, polyester or polyimide. The intense heat generated by hot crimping causes the insulation to vaporize during crimping. Eliminating the production step of stripping the isolation increases productivity when making electrical connections. As no stripping is involved, no metal is removed which guarantees maximum strength.

Examples of Hot Crimping Applications
Hot Crimping has been used by major European electric motor manufacturers such as Bosch, Siemens and Volkswagen since 2011. This means that it is a relatively new, but very rewarding technology. For decades, these companies used machines or chemicals to strip the enamel coating from the ends of magnet wires before crimping them to copper ring terminals or sleeves. As described above, hot crimping in contrast vaporizes the insulation during the crimping of the wire and terminal or sleeve. By eliminating the stripping step, hot crimping enables these manufacturers to increase productivity.
Magnet wire is an insulated copper (or aluminum) electrical conductor used in electromagnetic equipment like motors and transformers. The wire is wound in coils to generate an electromagnetic field. A copper terminal, which can be coated with tin, nickel or silver, is attached to the free end of the wire so it can be connected to a source of electrical power. Hot crimping can join standard magnet wires, high-frequency magnet wire (for frequencies above 10 kilohertz) and uninsulated copper wires. Hot crimping can weld individual magnet wires as thin as 30 AWG (0.05 mm2) or a wire bundle as thick as 400 square millimeters (stranded or braided).
Most magnet wire is made from fully annealed, electrolytically refined copper. Aluminium magnet wire is less common. This is because it has lower electrical conductivity, and its cross-sectional area must be 1.6 times wider than copper wire to achieve comparable DC resistance.
Smaller-diameter magnet wire (20 AWG to 36 AWG) tends to have a round cross-section. Thicker wire is often rectangular (with rounded corners) or square to more maximize use of available winding space. These wires are also referred to as "hairclips" referring to their bent shape in electrical motors.
Hot Crimping has seen a large growth in the automotive market due to the electrification of the powertrain. High current connections from the battery to the inverter, from the inverter to the electrical motor and inside these components can all use Hot Crimping as a joining technology. The low electrical resistance will lead to lower temperatures for the parts in operation and will increase the reliability and electrical efficiency of the parts compared to conventional joining technologies.
Another growth market for Hot Crimping is renewable energy, where high electrical currents are often generated such as in windmills, water turbines and PV installations.
Improvement to Conventional Cold Crimping of Cable Shoes
Normal “cold” crimping makes a connection to the terminal or cable shoe by using only a mechanical clamping force. This can cause the contact to deteriorate due to stress relaxation. “Cold” crimping can also suffer from cavity corrosion. Good quality, hot crimping does not suffer from either of these problems.
Equipment & Operation
The worker uses a benchtop welder to place the coil wound with magnet wire into the machine, inserts open wire ends in the terminal and activates the weld cycle. Within milliseconds, the welding heads release enough current to produce a temperature of about 700°C at the terminal. This temperature is hot enough to vaporize the insulation and weld the wire ends to each other and the terminal. A MIYACHI EAPRO fume extractor exhausts the vapours.
Once welding is complete, two-stage cooling of the terminal begins. Within a few seconds, the terminal cools down to about 100 °C. After a few more seconds, it cools to 50° C and can be manually removed from the machine.
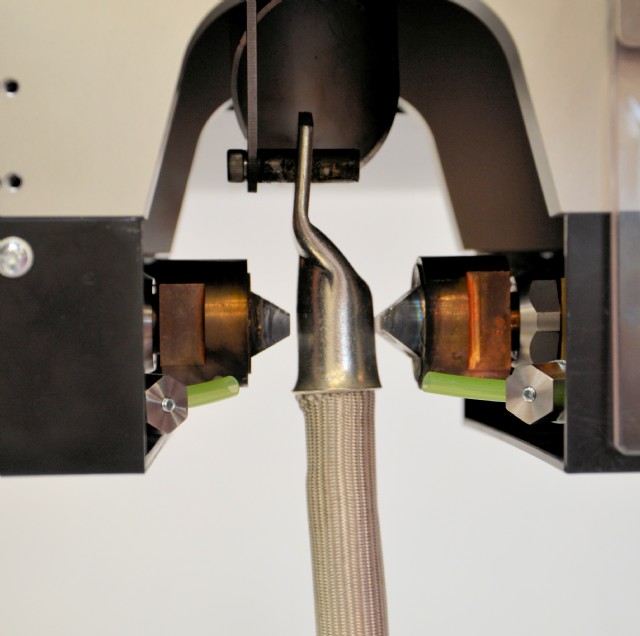
Semi-automated systems have a small pallet that moves the component into and out of the hot-crimping machine. This can be inline or can use a rotary table. The worker inserts the wire ends into the terminal, activates the machine and removes the component from the pallet after it has cooled. All welding data is stored in the machine and can be accessed easily. Manufacturers can use this data to quickly verify or change welding parameters or for product traceability.


