You are here
Laser Seam Welding
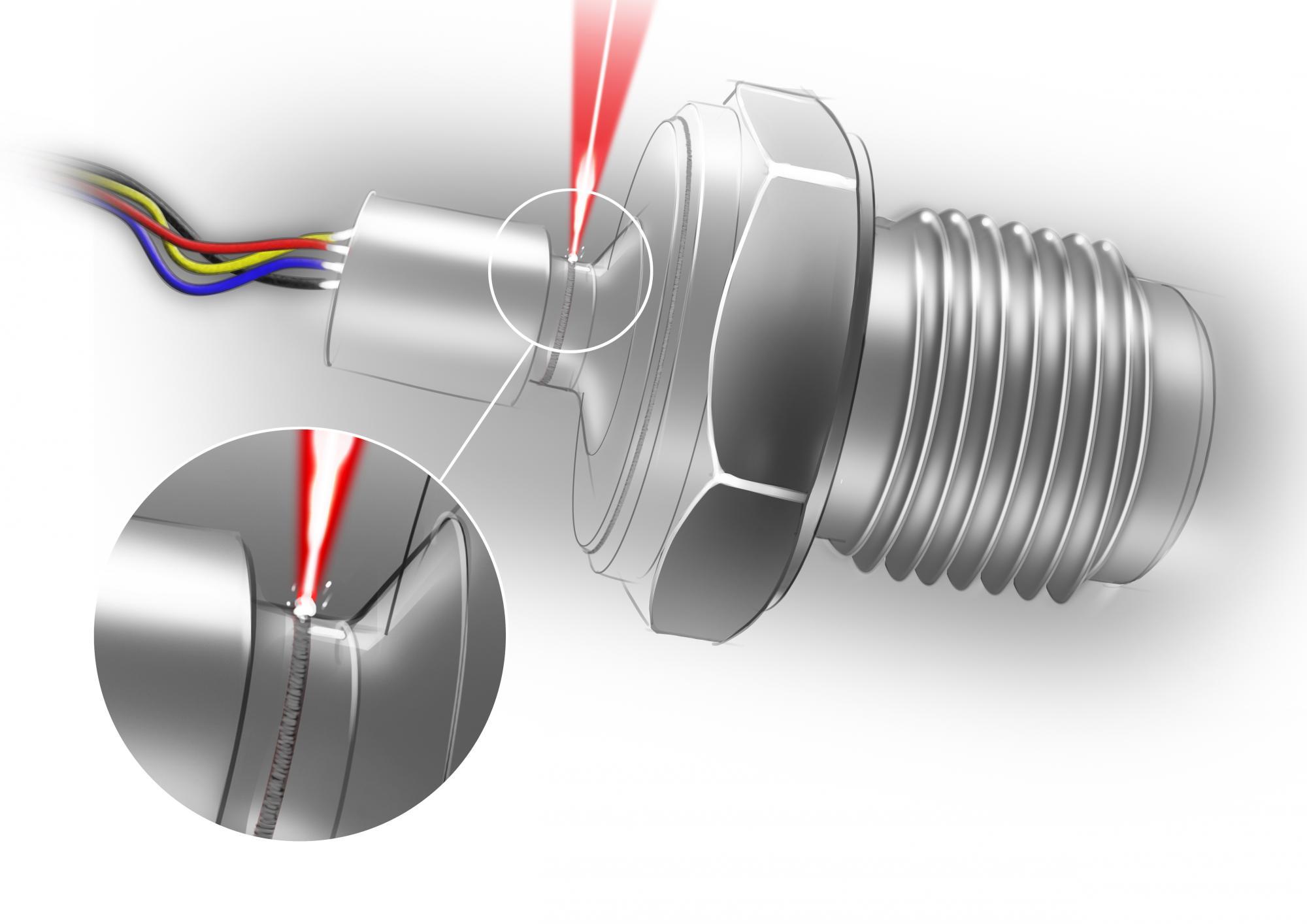
Laser Seam Welding is a joining technique used to weld multiple pieces of metal through the use of a laser. A laser produces a beam of high-intensity light which is focused into a single spot to provide a concentrated heat source which allows for narrow, deep welds and high welding speeds.
Seam Welding is a variation of spot welding. In laser seam welding, the part to be welded is moved or rotated under the focus head allowing laser spot welds to overlap. Key parameters for laser seam welding are the pulse repetition rate, measured in pulses per second (Hz) and the linear part travel rate or welding speed. Spot overlap percentage (a function of speed), pulse repetition rate and focused spot diameter are also used in the equation for determining the best laser for the job and for determining the total weld cycle time. Laser welding is used to make hermetic seam welds.
Laser Seam Welding Benefits:
- Small heat affected zone
- Contactless welding
- Very fast welding
- Low cost per weld for high volume seam weld application
Applications of Laser Seam Welding
There are two ways to deliver the energy, namely, in short pulses or continuously. One of the two types is chosen depending on the application. The process is used in both high and low volume applications, such as in the battery and medical industries.
Typical applications of laser seam welding include sensors, radar components, battery housing, conductors for thin film cells, pacemaker cases and insulin pump cases.