You are here
Parallel Gap Welding
Gap Welding is the process of bonding together two parts by placing both electrodes against the same surface on just one part. The weld current flows from one electrode, through the top part, and partially into the bottom part. It then returns to the power supply via the second electrode (see figure).
Gap Welding may be the only viable bonding method when electrode access can only access one part or the part materials preclude the use of pulsed YAG laser welding.
Parallel Gap Welding Applications
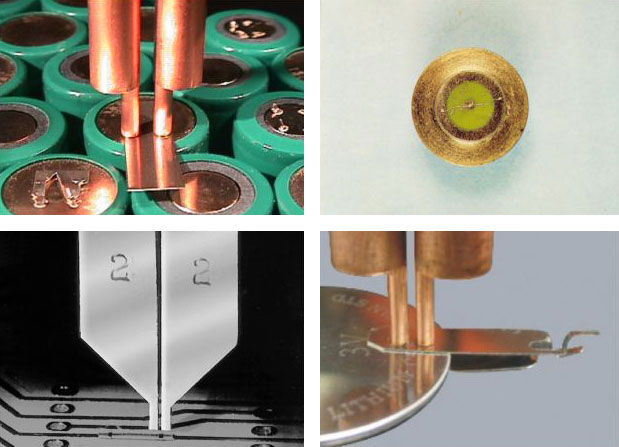
Benefits of Parallel Gap Welding:
- Welding of products that can only be approached from one side
- Products that are insulated on one side can be welded (PCB repair)
- Weld current does not pass through the complete body of the lower part
- Dual nuggets in one weld operation
Typical applications of Parallel Gap Welding include battery packs, medical or automotive sensor wires to PCBs, solar cells, hybrid or microwave circuitry, thin or thick film substrate, potentiometers and other miniature components, semi-rigid substrates and fine line printed circuit trace repair.







