You are here
Heat-Sealing/ACF Final Bonding
The process of creating electrically conductive adhesive bonds between flexible and rigid circuit boards, glass panel displays and flex foils is referred to as Heat-Sealing or ACF Final Bonding. The essential characteristics of this process are the heating and cooling of the adhesive under pressure.
Small adhesive particles or spheres are suspended in the adhesive, which can be in the form of foil, flex or paste. Before bonding, the particles are separated using an adhesive isolating matrix. The parts to be joined are first brought together with the adhesive in between. Temperature, time and pressure are applied and cause plastic deformation of the adhesive and compression of the particles. The particles that are trapped between the conductors form a conductive interface between the pads on the two mating surfaces and conduct only along the Z-axis. Subsequent cooling and full curing of the adhesive while still in the compressed condition stabilise the joint.
Applications in Heat-Sealing/ACF Final bonding
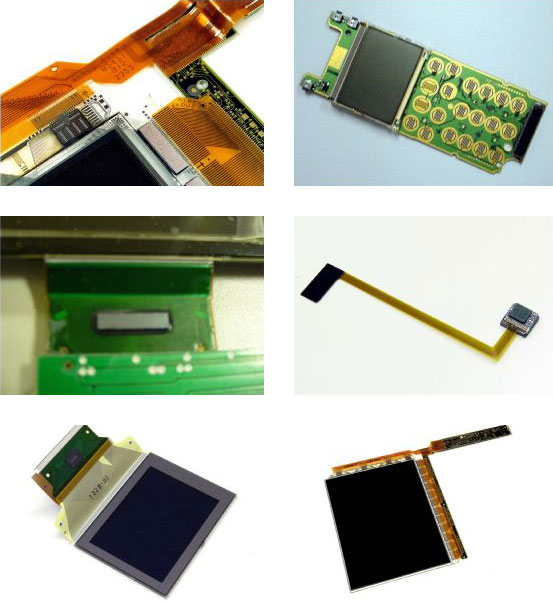
Anisotropic Conductive Adhesive Bonding is divided into two techniques:
- Heat-Seal Bonding The Heat-Seal Bonding process is applied with flex materials using an adhesive pre-printed onto the connector foil / flex foil.
- Anisotropic Conductive Film bonding The ACF Bonding process is used for fine-pitch applications (> 30 micron) as it has smaller sized particles than in heat seal connectors (HSCs).
Benefits of Heat-Sealing/ ACF Final bonding:
- Lead-free process
- Smallest pitch >30 micron possible
- Flux-free process
- Electrical connections to glass substrates
- No cleaning required after process
- Low process temperatures